Robotics scientists at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) achieved what many considered science fiction: the creation of the world’s first jet-powered flying humanoid robot, known as iRonCub3. This robot is not merely a mechanical figure designed to mimic human movement; it represents a groundbreaking integration of aerial propulsion systems, artificial intelligence, and human-like articulation, allowing it to lift off the ground and hover in controlled flight. Unlike drones or unmanned aerial vehicles that have dominated aerial robotics for decades, iRonCub3 combines the full complexity of human-like limbs, a humanoid body, and real-time decision-making, marking a leap in robotic engineering.

Its successful first flight, though brief, has demonstrated that humanoid robots can move beyond the constraints of the ground and perform tasks in vertical space, opening up possibilities for applications that range from disaster response and industrial inspection to future space exploration. The development of iRonCub3 signifies not only an engineering triumph but also a philosophical shift in robotics, where machines are no longer passive assistants but potentially autonomous partners capable of navigating environments in ways previously reserved for humans.
Table of Contents
iRonCub3
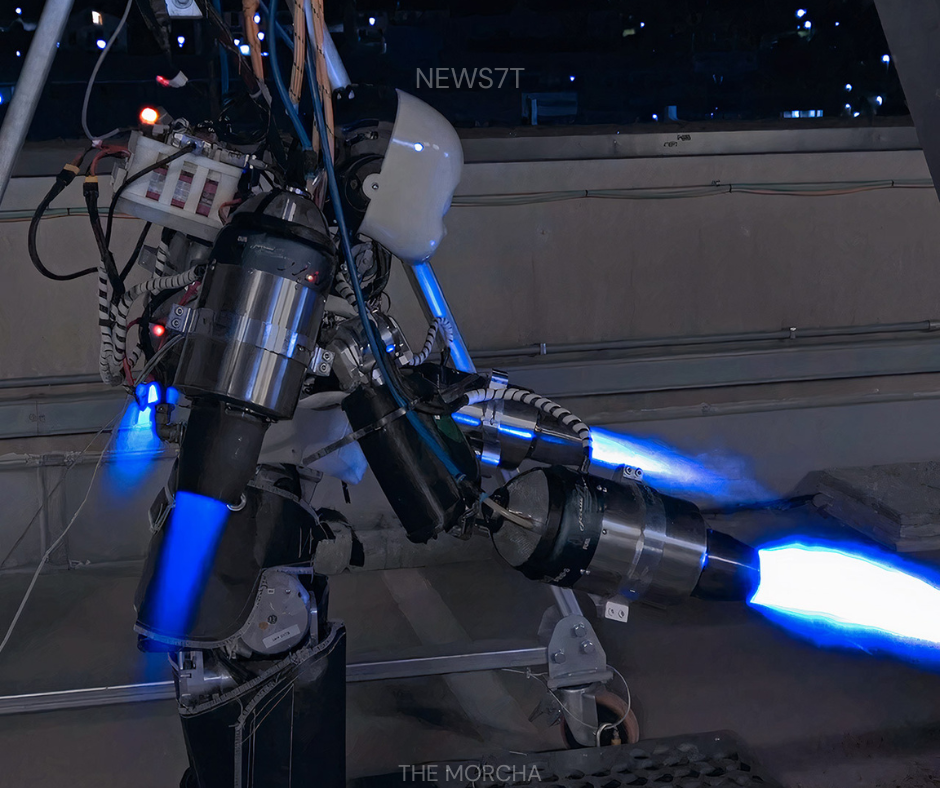
The iRonCub3 is a marvel of engineering that integrates multiple high-tech systems into a humanoid form, making it capable of controlled flight. Its titanium skeleton and lightweight composite materials provide structural integrity while remaining agile enough to support the dynamic movements of flight. Four mini jet engines, mounted on its arms and back, generate sufficient thrust to lift the robot and allow it to hover or maneuver in place. What sets iRonCub3 apart from other robots is its AI-driven balance and stabilization system, which continuously monitors hundreds of parameters, including orientation, thrust output, limb positioning, and environmental conditions.
This allows the robot to maintain stability in ways that would be impossible for a human or even a traditional drone. Additionally, its sensor suite includes gyroscopes, accelerometers, and pressure sensors, which feed real-time data into neural network algorithms that adjust flight in milliseconds. Together, these technologies make iRonCub3 a pioneering example of a humanoid robot that can not only walk or manipulate objects but also fly, bridging the gap between terrestrial robotics and aerial mobility.
Engineering Challenges in Human-Like Flight
Designing a humanoid robot capable of flight presented engineers with challenges that are fundamentally different from those encountered in drone development. Human-like bodies have irregular shapes, flexible limbs, and a variable center of mass, all of which complicate flight stability. Traditional flight control algorithms, designed for symmetric drones, cannot compensate for the constantly shifting balance of a humanoid form. Engineers had to develop custom multi-body dynamics models to simulate every possible movement and its effect on flight stability before attempting real-world tests.
Heat management was another critical challenge, as jet thrusters generate high temperatures that could damage the robot’s circuits or sensors if not properly shielded. The robot also needed to maintain structural integrity while accommodating the stresses of vertical lift-off, hovering, and potential minor collisions. Furthermore, the AI algorithms had to anticipate and react to fluctuations in thrust, body movement, and environmental conditions in real time, requiring hundreds of calculations per second. Overcoming these obstacles demonstrates the enormous complexity involved in translating a humanoid form into an aerially capable, autonomous machine.
AI Integration and Real-Time Control
The AI system in iRonCub3 is the brain that allows the robot to perform tasks that would otherwise be impossible. Unlike pre-programmed drones, this AI continuously interprets sensory data, including feedback from gyroscopes, accelerometers, and pressure sensors, to maintain balance and stability. Neural networks are trained to predict the effects of limb movement on flight dynamics, allowing the robot to make micro-adjustments hundreds of times per second. This ensures that its body remains upright, arms do not destabilize the flight, and the robot can hover or perform controlled movements even in variable conditions.
The AI also coordinates the four jet engines in a synchronized manner, distributing thrust as needed to counteract shifts in the robot’s center of gravity. This integration of AI with mechanical systems demonstrates the possibility of autonomous aerial humanoids, capable of both reacting to real-time challenges and performing tasks with human-like dexterity. The sophistication of this AI makes iRonCub3 not just a flying machine but an intelligent, adaptable system that can potentially operate in environments unsafe for humans.
Flight Mechanics and Jet Propulsion
iRonCub3’s flight mechanics rely on four mini jet engines strategically positioned to provide vertical lift, stability, and maneuverability. These engines expel high-velocity gases that lift the robot and enable it to hover in place, while the AI constantly adjusts power levels to compensate for weight distribution and movement. Unlike conventional jetpacks, iRonCub3 must coordinate thrust across multiple points while also controlling the orientation of its arms, legs, and torso.
This creates a highly dynamic system where even minor limb movements can affect stability, requiring precise, real-time calculations. The robot’s ability to hover, maintain posture, and make micro-movements in the air is unprecedented in humanoid robotics. In future iterations, directional flight, longer duration hovering, and obstacle navigation are expected to be added, transforming the robot from a prototype into a functional tool for various applications. These mechanics illustrate how engineers have merged aerospace principles with humanoid robotics to create a machine that is both flexible and powerful.
Applications in Disaster Response
Flying humanoid robots like iRonCub3 could revolutionize disaster response operations. Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and wildfires often create conditions that are too dangerous for humans to navigate. A robot capable of vertical flight can bypass debris, enter collapsed structures, and reach areas that would be otherwise inaccessible. Its humanoid form allows it to manipulate objects, carry supplies, or even stabilize unstable structures, while AI sensors provide real-time situational analysis.
In addition, such robots could relay critical data to rescue teams, assess structural damage, and identify hazards, reducing human risk and improving operational efficiency. The combination of aerial mobility and human-like dexterity makes iRonCub3 uniquely suited to these high-risk environments, where conventional drones or robots may struggle to perform precise interventions. In this way, flying humanoid robots have the potential to save lives and enhance emergency management capabilities worldwide.
Industrial and Hazardous Environment Applications
Beyond disaster zones, flying humanoid robots have the potential to transform industrial operations in hazardous environments. Locations such as nuclear power plants, offshore oil platforms, chemical facilities, and construction sites often present dangers to human workers. Robots capable of hovering, maneuvering, and performing precise manipulations could inspect equipment, conduct repairs, and monitor critical systems without exposing humans to risk.
The humanoid design allows for interaction with tools and equipment designed for human use, enabling robots to perform tasks that conventional drones or robotic arms cannot. By integrating mobility, dexterity, and AI-driven decision-making, iRonCub3-like robots could significantly improve workplace safety and efficiency, enabling industries to manage high-risk operations with reduced human intervention.
Space Exploration Potential
Flying humanoid robots also hold promise for space exploration. Planetary environments often have unpredictable terrain, obstacles, and low gravity, posing challenges for wheeled or tracked rovers. A humanoid robot capable of flight could navigate craters, rocky surfaces, and structures with greater flexibility. Its AI systems could manage aerial movement and manipulation simultaneously, allowing it to conduct repairs, gather samples, and assist astronauts in tasks that require human-like dexterity.
Moreover, its humanoid form enables interaction with tools, machinery, and spacecraft systems designed for humans, bridging a critical gap in space operations. The development of iRonCub3 serves as a prototype for autonomous robots that can perform both aerial and manual tasks in extraterrestrial environments, offering a glimpse into the future of robotics beyond Earth.
Ethical Considerations and Safety
While the technological achievements of iRonCub3 are remarkable, they raise important ethical and safety considerations. The use of jet propulsion near humans or populated areas introduces inherent risks that must be carefully managed. Furthermore, autonomous decision-making in unpredictable environments poses questions about liability and accountability if accidents occur.
Ethical concerns also arise when considering potential military applications, surveillance uses, or the replacement of human labor in sensitive tasks. To address these challenges, developers emphasize the need for robust safety protocols, ethical guidelines, and regulatory oversight. Ensuring that flying humanoid robots serve humanity positively, without introducing new risks or inequities, is as critical as perfecting their technical capabilities.
Limitations and Future Challenges
Despite its groundbreaking design, iRonCub3 faces several limitations. Its reliance on jet engines requires significant fuel, limiting flight duration, and making continuous operation impractical for now. The complexity and cost of production restrict its deployment to research or specialized applications. Environmental factors such as wind, temperature, or obstacles can affect stability, necessitating advanced sensing and navigation technologies.
To overcome these issues, researchers are exploring hybrid propulsion systems, improved AI control algorithms, and advanced lightweight materials. The next generation of flying humanoid robots may incorporate longer flight durations, enhanced maneuverability, and greater autonomy, enabling practical applications in both civilian and industrial contexts.
Introduction to China’s Robot Mall
While Italian engineers push the boundaries of humanoid flight, China is pioneering the integration of robots into everyday life. In August 2025, Beijing’s E‑Town district inaugurated the world’s first humanoid robot mall, a four-story, 4,000-square-meter complex designed to showcase, sell, and service a variety of robots. The mall combines commercial, educational, and demonstration spaces, allowing visitors to experience robots performing daily tasks, interacting socially, and assisting with work.
Beyond retail, the mall serves as a platform for research, networking, and collaboration among robotics developers, investors, and consumers. By bringing robots into a visible, interactive environment, China is accelerating public familiarity and acceptance of robotics, positioning itself at the forefront of global robotics adoption and innovation.
Structure and Offerings of the Robot Mall
The Robot Mall is organized into multiple zones, each serving a specific purpose. The sales zone displays a wide range of robots, from humanoid assistants and industrial robots to companion and educational units. The demonstration zone allows visitors to interact with robots in real-life scenarios, such as cafés, classrooms, and retail environments, showcasing their abilities to serve, entertain, or educate.
The service zone provides maintenance, repair, and software updates, ensuring that robots purchased or tested in the mall can remain operational. Finally, the mall hosts industry collaboration events, including product launches, networking meetings, and exhibitions, connecting developers with investors and end-users. This comprehensive approach ensures the mall is more than a retail center; it is an ecosystem for technological engagement, adoption, and innovation.
Making Robotics Accessible to the Public
One of the Robot Mall’s key objectives is to demystify robotics for the public. Visitors can engage with humanoid robots that serve food, pour beverages, assist with shopping, or perform educational tasks, experiencing firsthand how robots can enhance daily life. Affordable models designed for households coexist alongside high-end professional robots, catering to a wide range of consumers.
By enabling direct interaction, the mall allows people to understand the practical benefits, limitations, and possibilities of robotics, fostering a sense of familiarity and trust. This accessibility is crucial for mainstream adoption, helping society embrace robotics as a functional and integrated part of daily life rather than a futuristic novelty.
Consumer Engagement and Experience
Consumer engagement at the Robot Mall goes beyond mere observation. Interactive zones allow visitors to test robots, adjust their behavior, and witness autonomous decision-making in real time. Visitors can see robots prepare beverages, assist with retail tasks, or perform social interactions, providing an immersive experience that emphasizes the robots’ utility and intelligence.
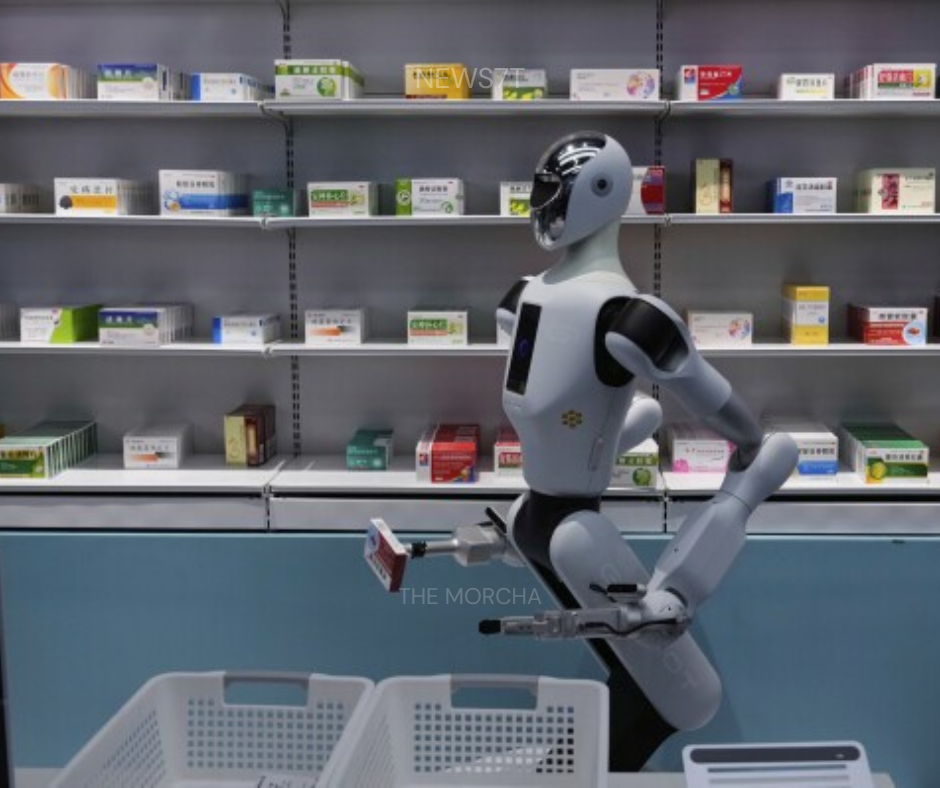

By enabling this hands-on interaction, the mall educates the public about robotics, fosters curiosity, and encourages the adoption of robotic solutions in homes, schools, and workplaces. The experiential design of the mall makes robotics tangible and relatable, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical understanding.
Supporting Local Robotics Industry
The mall also plays a strategic role in promoting domestic robotics innovation. It provides a platform for startups and established manufacturers to showcase products, receive consumer feedback, and connect with investors. Government support, in the form of subsidies, grants, and innovation zones, complements this initiative, accelerating research and commercialization. By providing visibility to local brands and fostering collaboration, the mall strengthens China’s robotics ecosystem, ensuring sustained growth in both consumer and industrial markets. This focus on nurturing homegrown innovation positions China as a global leader in robotics development and adoption.
Robotics in Daily Life
The Robot Mall exemplifies the increasing integration of robotics into daily life. Robots are now performing tasks traditionally done by humans, including serving in cafés, providing educational support, and assisting with home chores. Their presence in commercial spaces introduces society to the possibilities of human-robot collaboration, while household models help with mundane or repetitive tasks. By showcasing robots in practical applications, the mall reinforces the idea that robotics is not a distant or speculative technology but a present reality capable of enhancing efficiency, safety, and quality of life.
Economic and Social Implications
The emergence of flying humanoid robots like iRonCub3 and commercial robotics hubs such as China’s Robot Mall carries profound economic and social implications. Economically, these robots can significantly increase efficiency, performing dangerous or repetitive tasks in industries like disaster response, chemical plants, mining, and manufacturing. By reducing human exposure to hazardous environments, they can lower workplace accidents, save costs, and create entirely new markets for robotics development, AI programming, maintenance, and support services.
At the same time, the rise of autonomous robots raises concerns about job displacement, particularly in sectors where human labor may be replaced by machines. Without proper reskilling programs and equitable access to opportunities, automation could exacerbate social inequality and economic divides.
On the societal front, humanoid robots introduce ethical and legal challenges. Questions about responsibility arise if a robot makes a mistake in a critical task, and public concerns about privacy, surveillance, and human interaction must be addressed. Society will also need to adapt to human-robot collaboration, ensuring safety, trust, and effective integration into daily life and workplaces.
Countries leading in robotics technology may gain global economic and strategic advantages, while others risk falling behind if they fail to invest in innovation and workforce development. Ultimately, flying humanoid robots signal a transformative era in which humans and intelligent machines must coexist responsibly. When combined with strong regulations, ethical guidelines, and public education, robotics can enhance productivity, safety, and quality of life while minimizing social disruption.
Future Prospects in Robotics
The future of robotics is being shaped by the convergence of technical innovation and societal integration. Flying humanoid robots could soon perform complex rescue missions, industrial inspections, or space exploration tasks autonomously, while commercial spaces like the Robot Mall will introduce robotics to homes, schools, and workplaces.
As AI and materials technology advance, robots will become increasingly capable, flexible, and accessible. Human-robot collaboration may become the norm, with robots serving as partners, assistants, and collaborators across multiple domains. These developments suggest a future in which robotics is fully embedded in everyday life, enhancing productivity, safety, and human experience.
Bridging Science and Society
The development of iRonCub3 and the establishment of China’s Robot Mall illustrate two complementary trajectories in robotics: pushing the boundaries of technical capability and ensuring societal accessibility and adoption. iRonCub3 demonstrates the heights of engineering innovation, combining AI, flight mechanics, and humanoid design to create a machine capable of unprecedented mobility and autonomy.

Meanwhile, the Robot Mall shows how robotics can enter mainstream life, enabling consumers to interact with, learn about, and integrate robots into daily routines. Together, these innovations reveal a future in which robots are not only tools but collaborators, capable of enhancing human safety, efficiency, and quality of life. This era represents a paradigm shift, moving robotics from laboratories into the heart of society and signaling a world where humans and robots coexist, complementing each other’s strengths in everyday life.


